Vacancies Stall Progress and Inflate Costs
Critical IT roles such as cloud engineers, EMR specialists, security analysts, remain open for 90–120 days, delaying migrations, AI initiatives, and security upgrades while driving up project budgets
Skills-First Hiring Sharpens Recruitment
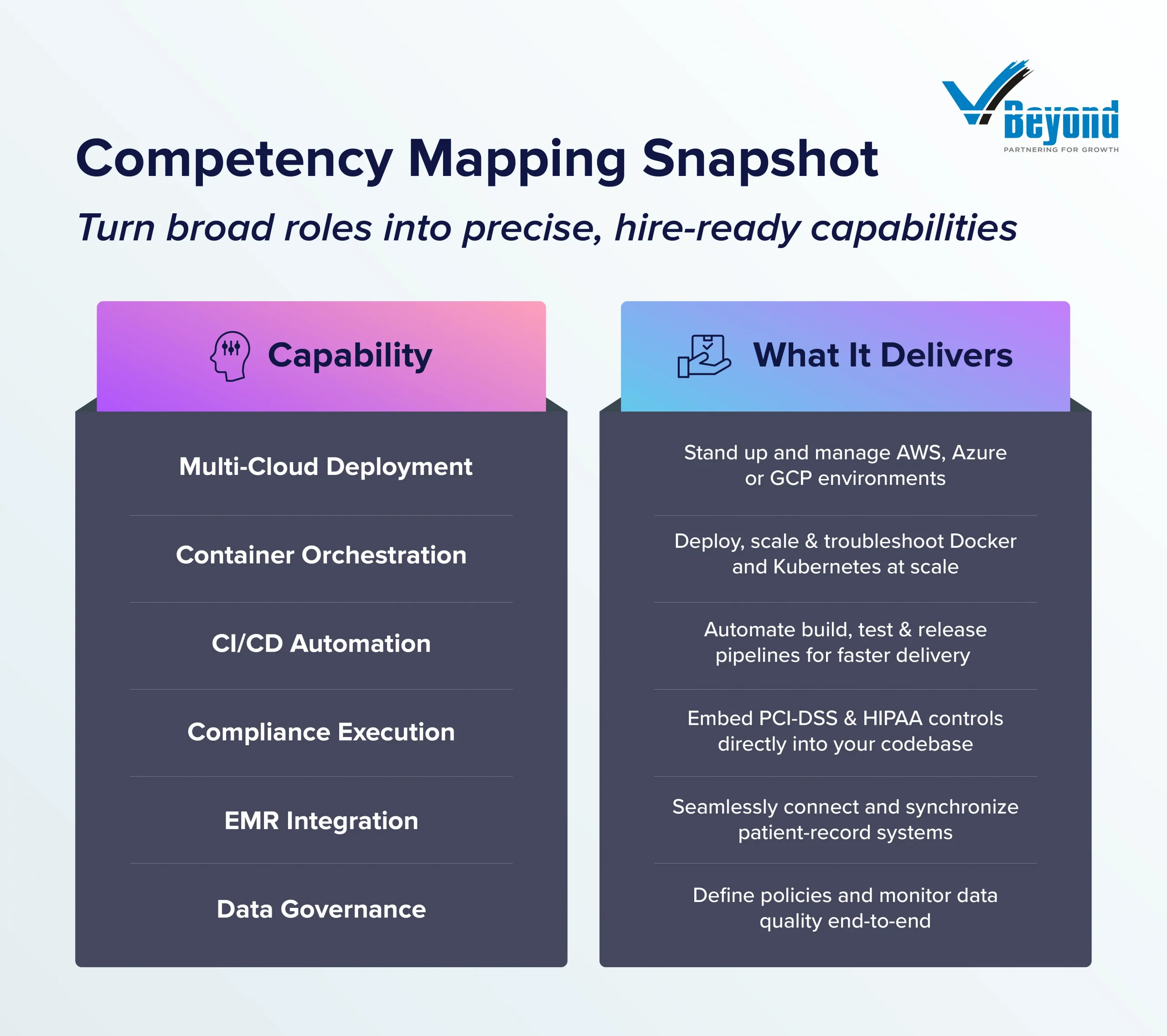
Defining discrete competencies (e.g., “FHIR API design,” “container orchestration”) enables targeted sourcing, flexible gig engagements, and objective scorecards, widening the candidate pool and reducing mismatch.
Tech-Driven Talent Acquisition Boosts Efficiency
AI-powered screening, predictive engagement analytics, and integrated ATS/CRM systems cut resume review by nearly half, surface passive talent, and maintain compliance in regulated environments.
Partnerships and Internal Learning Close Gaps
Alliances with universities, bootcamps, and consortiums expand pipelines, while in-house academies, mentorships, and micro-learning modules upskill existing teams—lowering vendor spend and improving ROI.
Digital transformation in finance and healthcare has accelerated sharply, driven by cloud migrations, AI-driven services, and ever-tighter security demands. Yet, while organizations race to deploy advanced systems, they confront a persistent shortage of specialized talent. Engineers who can build secure, compliant architectures and analysts who can turn vast data streams into actionable insight.
Banks and insurers face mounting regulatory burdens like GDPR, Basel III, SOC 2, that require staff with both deep technical expertise and domain knowledge. Health systems must balance HIPAA-secure patient records with AI-enabled diagnostics and telehealth platforms. The result? Critical IT roles remain open 90–120 days on average, far exceeding the 60-day benchmark, and digital initiatives stall under resource constraints.
This blog unpacks the market forces behind today’s talent squeeze, explores the costs of unfilled positions, and presents a step-by-step playbook: adopting skills-first hiring, using AI-powered recruiting, forging strategic partnerships, and building in-house training programs. By the end, you’ll have a clear framework to close the tech skills gap, accelerate project delivery, and protect both compliance and customer experience.
Introduction: Caught in the Tech Talent Squeeze
Financial institutions and health systems race to roll out cloud infrastructures, embedded analytics, and secure networks. Yet the pool of engineers skilled in multi-cloud environments, machine-learning pipelines, and threat detection remains limited. Recruiters now contend with steep salary demands and prolonged search cycles for each vacancy.
Banks and care providers face extra requirements of certified security experts, EMR integration specialists, and compliance officers who understand global data regulations. These credentials shrink the roster of eligible applicants, driving critical roles open for 90 to 120 days—well above the 60-day benchmark. As digital projects stall, budgets swell, and operational risks rise.
Market forces narrowing the candidate pool
Global talent markets tightened under low unemployment and aggressive hiring by technology giants and consulting firms. STEM graduation rates have not kept pace with demand for software engineers, data scientists, cybersecurity analysts, and cloud architects. As BFSI and healthcare recruiters compete for the same small cohort of specialists, salary expectations climb, and time-to-fill metrics stretch beyond industry benchmarks. Extended vacancies stall digital projects and inflate recruitment budgets.
Why do BFSI and healthcare face unique shortages?
Regulatory and compliance mandates in finance and health create additional hurdles for talent acquisition. Roles often require certifications such as CISSP, CISM, or health-IT credentials, narrowing the eligible candidate pool. Healthcare providers need specialists who understand EMR systems and interoperability standards, while banks and insurers seek security experts versed in SOC 2 and Basel III. These domain-specific requirements shrink the effective pipeline, intensifying the BFSI tech talent shortage and widening the gap between open roles and qualified hires.
Understanding the Tech Talent Gap
Understanding these drivers is the first step in closing the tech skills gap in BFSI and Healthcare. Below, we examine how market forces, evolving skill requirements, and sector-specific vacancy rates create acute hiring challenges.
Market forces driving record hiring pressure
Demand for specialized engineers and analysts has surged as digital initiatives accelerate. Financial firms ramp up cloud migrations, deploy real-time fraud monitoring, and embed fintech APIs. At the same time, health systems roll out telehealth platforms, interoperable EMRs, and AI-assisted diagnostics. These parallel waves pull from the same pool of cloud architects, security experts, data scientists, and software engineers. With STEM unemployment at historic lows and startups competing aggressively, organizations now contend with stretched time-to-fill metrics and rising offer-rejection rates.
Shifting skill requirements in cloud, AI, cybersecurity and data analytics
Skill sets have progressed well beyond basic coding or network administration. Recent roles demand multi-cloud proficiency such as Azure or AWS alongside container orchestration (Kubernetes) and production-grade machine-learning pipelines. Cybersecurity positions require expertise in zero-trust models, intrusion detection systems, and automated incident response. Data analytics roles blend ETL mastery, real-time streaming insights, and strict GDPR/HIPAA compliance. This evolution deepens the Healthcare IT skills gap and aggravates the BFSI tech talent shortage, as legacy IT teams rarely possess these emerging capabilities.
Comparative snapshot of vacancy rates in BFSI versus healthcare
According to the April 2025 JOLTS report, roughly one in twenty-four IT roles in finance and closer to one in seventeen in healthcare remain unfilled. Filling data-engineer positions often takes around three months, while securing EMR-integration specialists can stretch toward four months. Added credential requirements and regulatory clearances for patient-data handling push these timelines further, often beyond two months. This persistent staffing shortfall threatens digital project schedules and overall operational resilience.
Consequences of Unfilled Roles
When organizations fall short in closing the tech skills gap in BFSI and Healthcare, the ripple effects surface quickly. Unfilled positions leave critical initiatives under-resourced and expose teams to elevated risks.
Project delays and cost overruns on digital initiatives
Vacant roles slow development sprints and push deadlines out by weeks. A missing cloud engineer stalls a bank’s migration to microservices, forcing teams to maintain legacy systems longer and incur up to 15–20% higher infrastructure costs. In hospitals, delayed EMR upgrades keep staff tied to manual charting, increasing labor hours and operational expenses. These setbacks balloon budgets and sap momentum on high-visibility projects.
Compliance and security risks from understaffed IT teams
Lean cybersecurity teams struggle to apply patches, monitor real-time alerts, and conduct forensic analysis. Without a dedicated security analyst, intrusion detection systems may go unchecked for days, raising the likelihood of data breaches. Banks face steep penalties under Basel III and GDPR for uncontrolled vulnerabilities, while healthcare providers risk HIPAA fines and patient-record leaks. This compliance gap intensifies the Healthcare IT recruitment challenges and underscores critical exposure in both sectors.
Impact on patient care quality and customer experience
When digital portals glitch or telehealth platforms lag, patient satisfaction dips and trust erodes. Missed appointments due to system outages frustrate both clinicians and patients. Likewise, account-opening delays or mobile-app errors in banking drive customers to competitors. Caught between manual workarounds and off-hours incidents, service teams burn out. These service lapses highlight why Healthcare digital workforce solutions and robust Tech hiring strategies in BFSI are essential for sustaining quality and loyalty.
Adopting a Skills Based Hiring Framework
Organizations that move beyond rigid job titles can target the exact capabilities they need. A skills-based hiring framework breaks roles into discrete competencies, sharpens recruitment, and improves long-term retention.
Mapping critical competencies versus traditional role descriptions
Rather than advertising a monolithic “cloud architect” vacancy, companies must define the individual capabilities required: multi-cloud deployment, container orchestration, automated CI/CD pipelines, and compliance with PCI-DSS or HIPAA. In healthcare, “EMR integration” can be separated from “data governance,” so companies can source specialists who excel in one area without over-qualifying for others. This precision widens your candidate pool and aligns hires to project goals, reducing mismatch risk.
Designing flexible job architectures for hybrid and gig workers
Modern talent often prefers modular assignments over full-time roles. Companies must create “talent pods” that group related competencies such as AI model tuning and secure data handling into short-term engagements. A BFSI firm might assemble a cross-functional gig team for a six-week fraud-analytics sprint, then redeploy members on a customer-360 initiative. In hospitals, one could contract clinical-informatics experts to audit data workflows without hiring permanent staff. Flexible architectures accelerate delivery and contain costs.
Crafting competency assessments and scorecards
Replacing generic interview checklists with structured scorecards that rate candidates on specific skills can sharpen skill evaluation. For each competency, such as “threat-vector analysis” or “FHIR API design,” outline proficiency levels and sample tasks. During screening, assign real-world scenarios, so candidates might outline a zero-trust network for a bank or draft an interoperability plan for patient records. Scoring against clear anchors ensures objective evaluations and reveals training priorities for new hires.
Tapping into Technology for Talent Acquisition
AI-driven tools, advanced analytics, and integrated platforms are speeding up sourcing and streamlining candidate workflows. Let’s explore how these tools work together to shorten time-to-fill, boost offer acceptance rates, and maintain compliance in regulated hiring.
AI-powered sourcing and screening tools to boost efficiency
New age recruiters use AI in recruitment to scan hundreds of resumes in minutes, pinpointing candidates whose skills profiles such as cloud architecture, data analytics, or clinical-informatics, match predefined competency anchors. These tools highlight passive candidates by analyzing social-media activity and open-source code contributions. As a result, talent teams cut screening time by nearly half, freeing recruiters to engage high-value candidates and tighten pipelines.
Data-driven candidate engagement and predictive analytics
By tracking touchpoints like email opens, response times, interview feedback, organizations build engagement maps that reveal where candidates drop off. Predictive analytics models then forecast offer-acceptance likelihood based on historical patterns: industry tenure, certification mix, or interview-to-offer ratios. BFSI and healthcare firms use these insights to tailor outreach cadence and messaging, boosting conversion rates and shortening time-to-fill for niche roles.
Integrating talent platforms with ATS and CRM systems
Seamless integration between AI sourcing platforms, applicant-tracking systems (ATS), and CRM tools ensures a single source of truth for candidate data. When a resume flags a “FHIR API design” expert, the ATS automatically schedules assessments and populates scorecards. Meanwhile, the CRM tracks stakeholder communications—hiring managers’ feedback or compliance approvals, so recruiters maintain audit trails for regulated roles. This unified workflow underpins a skills-based hiring framework and accelerates high-volume campaigns without sacrificing precision.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Strategic alliances extend reach and deepen talent pipelines beyond traditional recruiting channels. By partnering with universities, bootcamps, and certification bodies, BFSI and healthcare organizations tap into networks of reskilling professionals who already possess core competencies.
Collaborations with universities, bootcamps and certification bodies
Forming direct links with academic programs and specialized training providers enables co-development of coursework for cloud, AI, cybersecurity, and health-IT certifications that align with your competency scorecards. Sponsors can offer capstone projects such as a live EMR-integration case or fraud-analytics sprint, while faculty guide students through real-world scenarios. Early engagement accelerates placement of graduates into entry-level and hybrid roles.
Industry consortiums and cross-sector talent pools
Joining forces with peer organizations to share candidate pipelines for scarce skills creates a finance-health consortium that maintains a common roster of data engineers, security analysts, and DevOps specialists. Consortium members co-host hackathons and skills challenges, establish benchmarks, and spotlight top performers. This collaborative approach spreads recruitment costs and ensures a steady stream of validated talent for all participants.
Co-investment models for apprenticeship and fellowship programs
Investing alongside training partners in structured, on-the-job learning programs allows apprentices to split time between classroom instruction and hands-on assignments, building microservices in sandbox environments or configuring secure health-data workflows under mentorship. Fellowship tracks place mid-career professionals into cross-functional rotations, from cloud migrations to compliance audits. Shared funding reduces upfront costs, while guaranteed placements secure ROI and strengthen workforce pipelines.
Upskilling and Reskilling for Future Readiness
Closing the tech skills gap requires more than hiring; it demands building capabilities from within. Strategic upskilling and reskilling equip your teams with the technical know-how and adaptability required for tomorrow’s challenges.
Internal learning academies and mentorship networks
Internal learning academies and mentorship networks blend structured coursework with hands-on projects. In a bank’s Cloud Academy, engineers cycle through multi-cloud workshops before honing skills in sandbox labs. Within a health system’s Digital Fellowship, junior IT staff work alongside clinical-informatics mentors to develop interoperable workflows. Executive sponsors and peer cohorts sustain momentum speeding skill adoption and reinforcing engagement.
Micro-learning modules and digital credentialing
Breaking complex topics into five- to ten-minute lessons makes them accessible via mobile or desktop portals. Modules focus on areas such as “HIPAA-compliant data pipelines” or “automated fraud-detection scripts,” with digital badges awarded upon completion that sync with LinkedIn profiles or your internal LMS. These bite-sized credentials allow hiring managers to confirm competencies at a glance and keep teams learning without pulling them away from mission-critical work.
Measuring ROI of training initiatives
Companies must track metrics that link learning investments to business outcomes. They should measure certification completion rates, time-to-proficiency on key toolsets, and internal mobility into high-priority roles. By comparing the cost of external contractors with that of in-house teams certified through the academy, organizations can calculate meaningful savings. For example, a healthcare provider could cut vendor spend by roughly 30 percent after reskilling professionals to manage telehealth deployments. Real-time dashboards must monitor retention gains and project velocity, ensuring every training dollar drives operational impact.
Measuring and Sustaining Talent Strategies
A playbook is only as good as its metrics and feedback loops. To sustain success in closing the tech skills gap, organizations must track key indicators, gather real-time market intelligence, and iteratively refine their approach.
Key metrics: time-to-fill, quality of hire, retention rates
Measuring time-to-fill for critical roles such as cloud engineers and EMR specialists highlights gaps in hiring efficiency, with a target of bringing average cycles down from 90–120 days to around 60. Assessing quality of hire involves comparing new-hire performance against predefined scorecards and project milestones. Correlating retention rates with competency development reveals that teams completing internal learning modules often see a lower churn in specialized tech roles. These metrics illuminate progress in closing the tech skills gap in BFSI and Healthcare and guide resource allocation.
Continuous feedback loops and talent market intelligence
Quarterly reviews bring hiring managers, HR leaders, and project sponsors together to examine pipeline health and pinpoint skill gaps. Leading organizations rely on external market data such as salary trends, certification rates, and competitor activity, to fine-tune sourcing approaches and adjust pay bands. Pulse-survey insights from recent hires, then inform improvements in candidate experience and onboarding materials. This data-driven cycle produces talent strategies that evolve with demands for AI recruitment, cybersecurity expertise, and healthcare digital workforce solutions.
Conclusion
Addressing the tech skills gap in BFSI and healthcare requires a multi-pronged approach: map competencies, deploy AI-driven recruiting, forge partnerships, and invest in continuous upskilling. By tracking metrics and maintaining agile feedback loops, organizations can fill critical roles faster, reduce costs, and protect compliance.
VBeyond Corporation partners with HR leaders and C-suite teams to design and execute skills-based hiring frameworks, integrate advanced talent platforms, and build bespoke learning academies.
Contact us today to discuss a tailored roadmap that tackles your BFSI tech talent shortage and secures a future-ready digital workforce.
FAQs
1. What is a skills-based hiring framework, and how does it differ from traditional recruitment?
A skills-based hiring framework breaks roles into distinct competencies such as “FHIR API design” or “zero-trust architecture”, rather than relying on broad job titles. This approach widens the candidate pool, enables targeted assessments, and reduces mismatch by aligning hires directly to the skills needed for specific projects.
2. How can AI-powered tools improve our time-to-fill for niche IT roles?
Modern AI sourcing platforms scan thousands of profiles in minutes, match expertise against your competency anchors, and surface both active and passive candidates. By automating initial resume screening and predictive engagement, you can cut review workloads by nearly half and focus your recruiters on high-value conversations.
3. What metrics should we track to ensure our talent strategies are effective?
Key indicators include time-to-fill (aiming for a 60-day cycle), quality of hire (via performance scorecards), and retention rates (benchmarking churn reduction after training programs). Coupled with real-time dashboards, these metrics highlight progress on closing skill gaps and guide resource allocation.
4. Which partnerships deliver the strongest talent pipelines for BFSI and healthcare?
Top-performing models include university and bootcamp collaborations such as co-developing cloud, AI, and health-IT curricula, and industry consortiums that pool scarce-skill candidates. Co-investment apprenticeships further strengthen pipelines by combining classroom instruction with on-the-job learning and guaranteed placements.
5. How can organizations measure ROI on upskilling initiatives?
Organizations can compare the cost of external contractors with that of internal teams certified through their academy to quantify savings. Also, they can track certification completion, time-to-proficiency, and internal mobility into critical roles. Monitoring these figures alongside project-velocity gains ensures every training dollar delivers tangible operational impact.


